<< Go back to the Research page.
Program Analysis
Research Overview
Software systems are getting larger and more complex. In a huge program with more than 100,000 lines of code, it is very difficult to find faults, without any supports of some tools. Technologies which helps to debug and maintain large softwares automatically and efficiently are expected.
One candidate approach would be program analysis. In our research group, we study Program Dependence Analysis that applied to program debugging and maintenance.
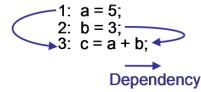
For example, in fig 1, the value of variable a defined at first statement is referred to at third statement, so a data dependency exists from the first statement to the third statment. As is the case with previous, a data dependency also exists from second statement to third statement. Dependency essentially represents appearance of the flow of data in a program, and we can obtain these dependencies by program analysis.
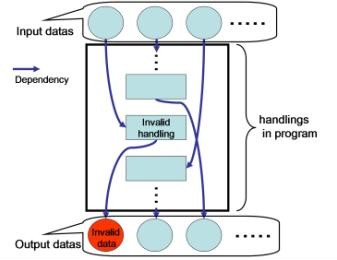
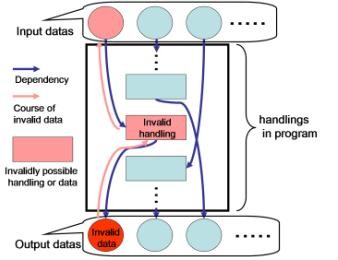
When system outputs a wrong result as fig2, we can restrict the part which would contain a bug to the part which have the dependency with the wrong output. So program analysis makes it easy to find faults as fig3.
Other subjects of research are "Change Impact Analysis" that identifies affected parts by change of program (For example, the affect of variable reference by change of variable name can be detectable.). We also study about "Alias Analysis" effective in dependence analysis of Object-Oriented Language.

Related Papers
- JAAT: A Practical Alias Analysis Tool for Java Programs
- Analysis and Implementation Method of Program to Detect Inappropriate Information Leak
- Dependence-Cache Slicing: A Program Slicing Method Using Lightweight Dynamic Information
Future Work
- Extension of the class of the target programming language.
- Improvement in the efficiency or correctness by algorithm modification.
- Evaluation of the system by applying the developed system to actual debugging work