Table of contents
1. Get the analysis result file of CCFinder
2. Execution of Gemini
3. Analyze code clones using Gemini
3.1 Clone Set Base Analysis
3.2 File Base Analysis
4. Link to other manuals
How to use Gemini
1. Get the analysis result file of CCFinder
At first, you have to get the analysis result file of CCFinder.
Following is the process.
You will find "get token-based code clone" label in the following screen.
Push its next button.
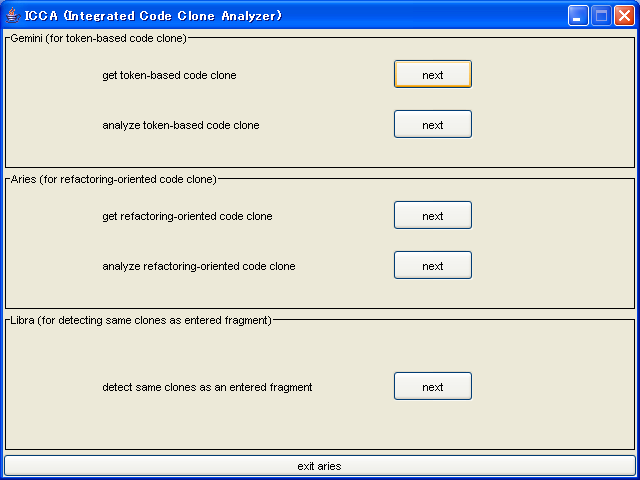
After pushing the button, following screen appears
If you have a list file that includes target files, push the "Load List" button.
If you don't have, you have to specify target files, push the "Select File or Directory" button.
After pushing these button, file selection dialog box appears.
You can select a file or directory.
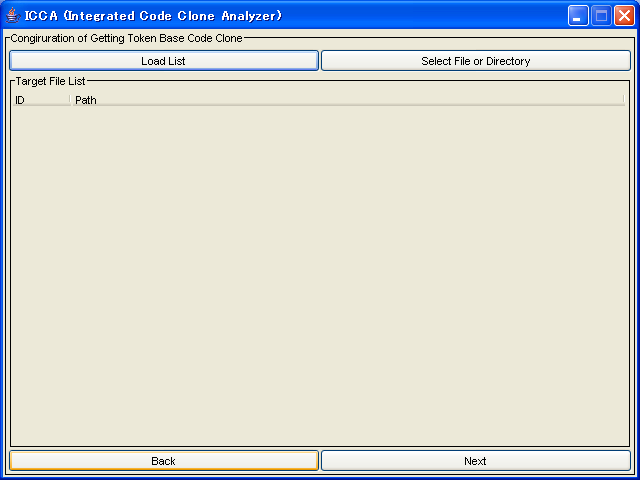
As following screen, if target files are listed, push next button.
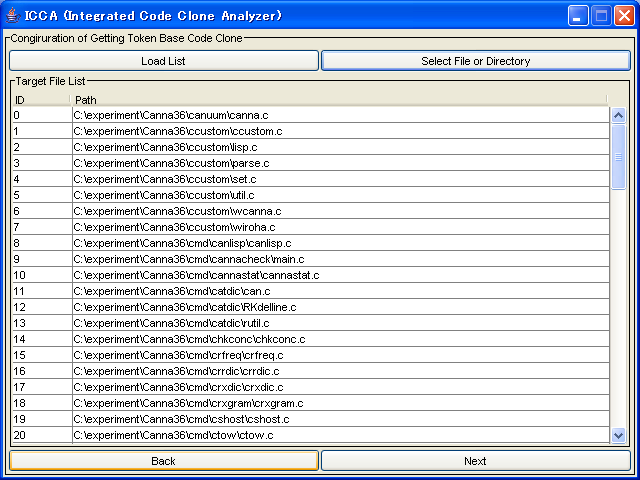
Here, you can specify options of code clone detection.
Following options are available.
- Minimum Clone Length
- This is the minimum token length that CCFinder detects(mandatory)
- Memory Resource Limit
- CCFinder devides source files according to this option(mandatory).
- Language Select
- This is the language of target files
- Detection Option
- This option decide what kind of code clones will be detected.(mandatory)
- Analysis Result File...
- This is the file path which Aries writes analysis result to.(mandatory)
- Other Options ...
- Here, you can specify other options that CCFinder has.
-
In many cases, you have to specify only "Language Select" and "Analysis Result File ..."
After specifying options, push the "Run CCFinder" button.
Then, after outputing log of detection, "Successfully Finished" appears.
Using this process, you can get the analysis result file of Aries.
In next phase, you analysis clone sets using Gemini.
Push OK button of "Successfully Finished" dialog box, and return initial screen.
2. Execution of Gemini
After returning to initial screen, you will find "analyze token-based code clone" label
Push its next button.
Then, the following configuration screen appears.
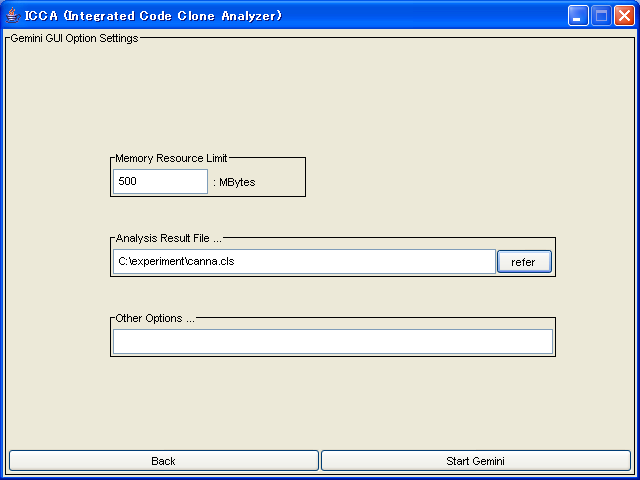
Here, following options are available.
- Memory Resource Limit
- This is the maximum memory size that Java VM uses(mandatory)
- Analysis Result File...
- This is the file path(the analysis result file of CCFinder) that you got above.(mandatory)
- Other Options
- This is other options(optional)
After specifying options, push the "Start Gemini" button,
3. Analyze code clones using Gemini
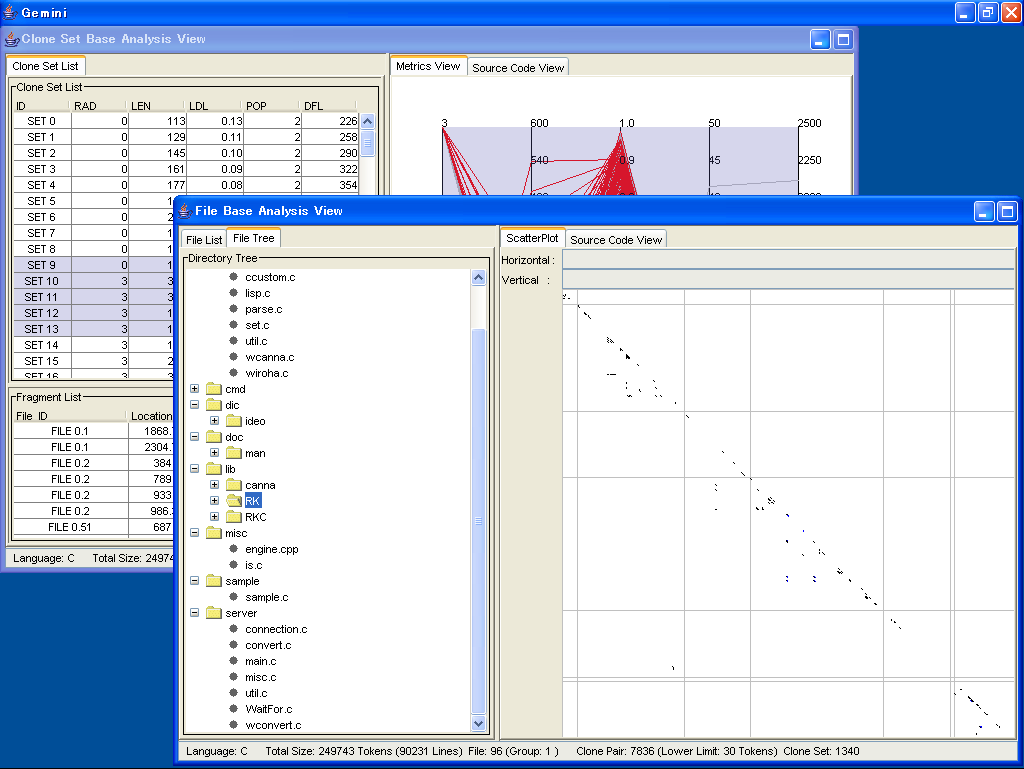
The above screen is a shapshot of Gemini.
Gemini has two type analyses.
One is the Clone Set Base Analysis, and the other is the File Base Analysis.
Both analyses have own internal frame.
2.1. Clone Set Base Analysis
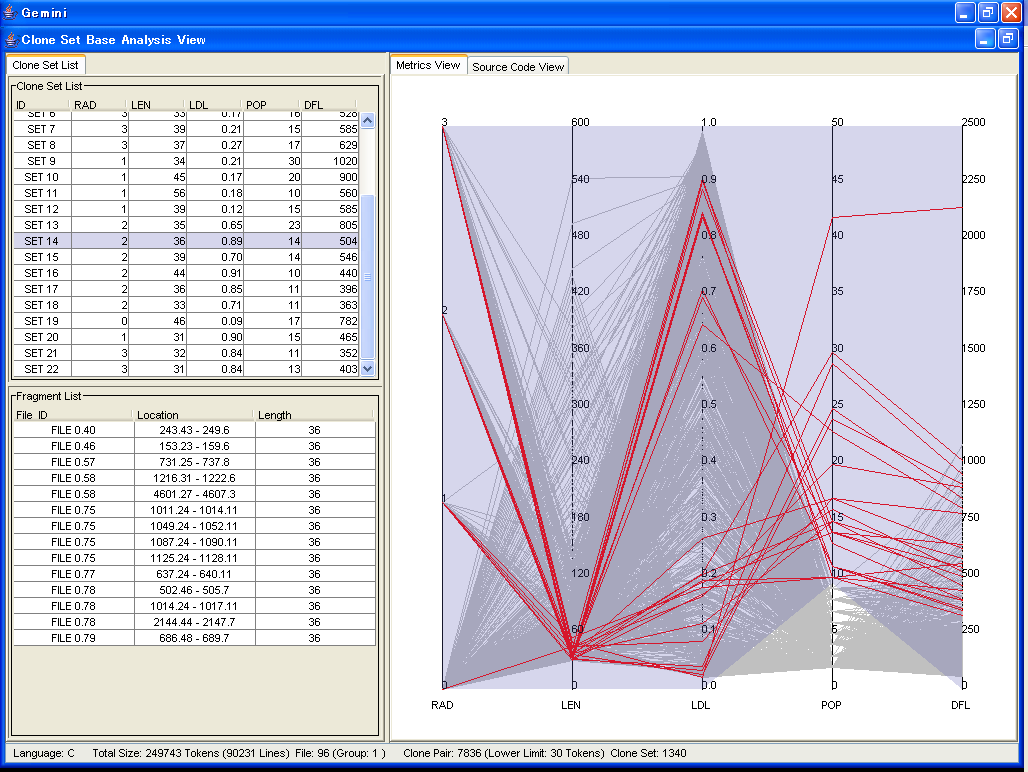
The above screen is the GUI for the Clone Set Base Analysis.
In the Clone Set Base Analysis, you can get your objective clone set by using the Metric Graph.
In the Metric Graph, you can change lower and upper limits of each metric, and filter clone sets(like above screen).
In this screen, we got clone set whose POP value is more than 10.
The result of filtering in the Metric Graph is reflected to the Clone Set List.
You can select clone sets that are listed in the Clone Set List.
All code fragment that are included in selected clone sets are displayed in the lower left corner.
Also, you can browse the source code of each code fragment.
Currently, following metrics are available in the Metric Graph.
- RAD(S)
- RAD(S) represents the range of the source code fragments of a code clone in the directory hierarchy,
when the source code is supposed to be stored in the hierarchical directory.
When all the code fragments of a clone class are located in one source file,
the RAD(S) value of the clone class is equivalent to 0.
When the code fragments of the clone class are located in multiple source files stored in one directory, the RAD(S) is 1.
If those sources files are stored in different directories,
then RAD(S) is the maximum depth of those sources measured from their common parent directory.
- LEN(S)
- LEN(S) means the average of token number that clone set S includes.
- RNR(S)
- RNR(S) reprensents the ratio how clone set S consists of non-repeated token sequenses.
For example, repeated token code clone is continous printf.
Most of these clones are rarely meaningful from our experiments.
Using RNR(S), we can filter such code clones.
- POP
- POP(S) means the number of code fragments which are included in clone set S.
- DFL
- DFL(S) indicates how many tokens would be removed from source codes if all code fragments are merged.
Also, you can export clone set data to a file in cvs format or CCfinder result file format.
Exporting in cvs format enables you to use other applications like MicroSoft Excel to analyse clone set.
Exporting in CCFinder result file enables you to treat only specified clone set data in the next usage of Gemini.
Clicking right mouse button on the Clone Set List, you can see the manu of exporting.
2.2. File Base Analysis
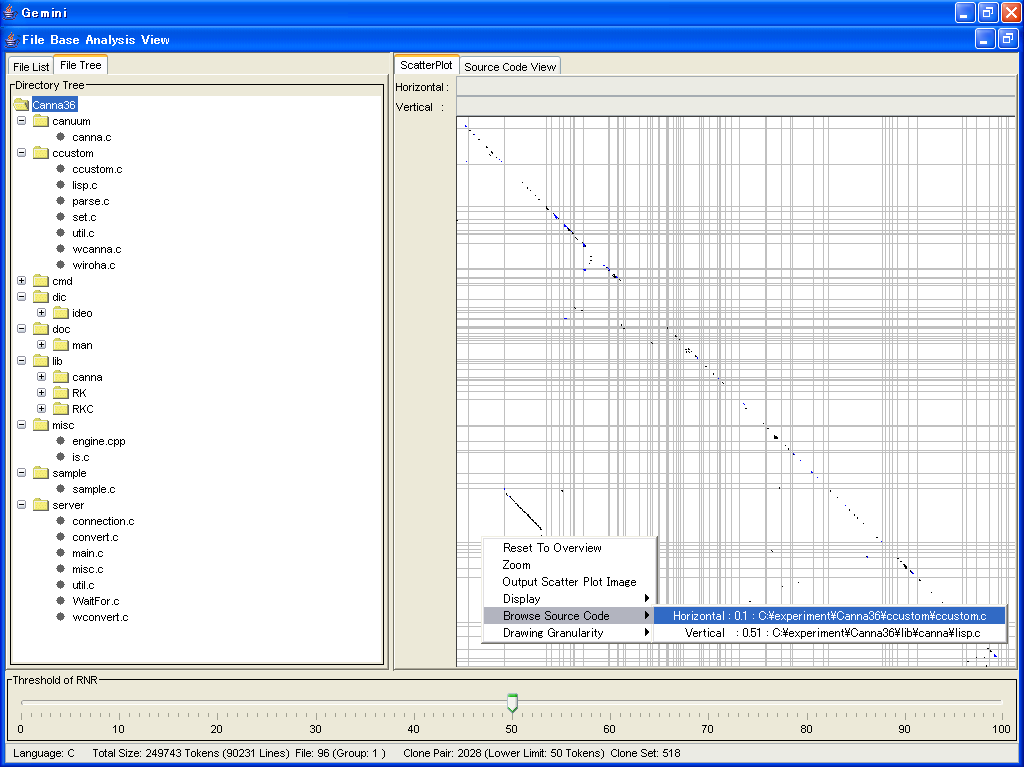
Above screen is the GUI for the File Base Analysis.
In the File Base Analysis, you can get your objective files using the Scatter Plot.
The Scatter plot shows visually where code clones exist.
The original point of scatter plot is upper left corner.
And, token sequence of source code is arranged on the both of horizontal and vertical direction from the original point in the same way.
Each cell of the Scatter Plot is checked if its corresponding horizontal and vertical tokens are identical.
A clone pair is shown as a diagonal line segment.
Also, the Scatter Plot has zoom function, which enables us to watch any portion of the Scatter Plot very closely.
In the File Base Analysis, you can select files basd on the value of RNR, which is an metric of code clone.
In the frame named "Threshold of RNR", you can adjust the value of RNR.
In this figure, the value of RNR is 50.
In this case, code clones whose value are more than 50 are drew with black, and others are drew with blue.
The Scatter Plot works with the File Tree.
If you select a directory in the File Tree, the directory is zoomed up in the Scatter Plot.
Also, if you click right button of mouse on the Scatter Plot, the menu appears.
Using this menu items, you can browse source codes of your objective files.
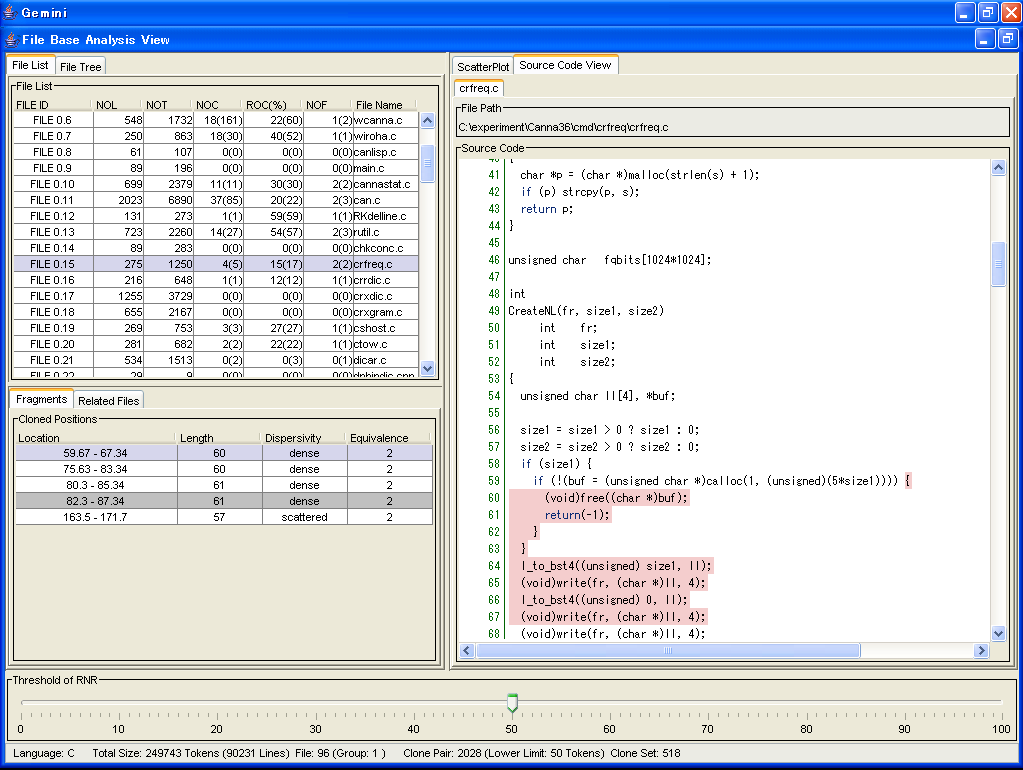
Also, in the File Base Analysis, you can get your objective files based on quantitative attributes.
Above screen is the File List.
In this File List, each file is characterized by 5 attributes,
and you can sort them base on their attributes
5 Attributes are followings.
- NOL
- This is the line number of the file.
- NOT
- This is the token number of the file.
Tokens in commends are not counted.
- NOC
- This is the clone number which are included in the file
- ROC
- This is the ratio how fhe file is cloned.
- NOF
- This is the number of files that share code clones with the file.
Metrics ROC and NOF have two values in each cell.
The value outside parenthesis is calculated by all detected code clones.
On the other hand, the value inside parenthesis is calculated by code clones whose RNR value is more than the threshold.
Also, all code clones that are include in the selected file are listed in the Fragment tab.
Each code clone in the Fragment tab is characterized by following 4 attributes.
- Location
- This is the location of the code clone.
The format is "StartLine.StartColumn - EndLine.EndColumn".
- Length
- This is the token number of the code clone.
- Dispersivity
- This means how the code clones are distributed in file system.
If all code clone are in a same file, "dense" is displayed.
If all code clone are in a same directory, "middle" is displayed.
In other cases, "scattered" is displayed.
Also, the highlight color is different by the degree of distribution.
"dense" is red.
"middle" is green.
"scattered" is blue.
- Equivalence
- This is the number of code fragment that is cloned with the code clone.
the background color of code clone whose RNR value are more than threshold is while, and the one of other code clones is gray.
You will find all files that shares some code clones with the selected file in the Related Files tab.
In the Related File tab, each files is characterized by following 4 attributes.
- NOL
- This is the line number of the file
- NOT
- This is the token number of the file
Tokens in comment are not counted.
- NOC(f)
- This is the clone number that the file shares with file f.
- ROC(f)
- This is the ratio how the file is cloned with file f.
After clicking right mouse button, "Set as Selected File" menu appears.
Using this menu, you set the file as selected in the File List.
4. Link to other manuals
to the manual of Aries
to the manual of Libra
to the introduction of ICCA









